In today’s fast-paced, technology-driven world, families are challenged to provide the right amount of attention and care their members need. While parents and family members are not always on the same page regarding priorities, one constant is family values.
Family values in Mexican culture are rooted in ancient history, but they are more prevalent today than ever. As a culture, Mexicans highly value family life and familial relationships. We will tell you what family means in Mexican culture, why it is so important to society, and how families and individuals can work together to improve their society. We will also discuss the role of the family in Mexican culture.

Exploring the Role Of The Family In Mexican Culture
The role of the family in Mexican culture. Family plays a central role in the lives of individuals, and strong family ties are emphasized. In Mexican culture, the family unit extends beyond just immediate relatives and often includes extended family members such as grandparents, aunts, and uncles. The family is seen as a source of support, love, and guidance throughout one’s life.
It is a common theme for multiple generations to live together or nearby, fostering a deep sense of unity and interconnectedness. Family gatherings and celebrations strengthen these bonds and maintain cultural traditions. The family is integral to Mexican culture and serves as a foundation for individual identity and community cohesion.
Importance Of Family In Mexican Culture
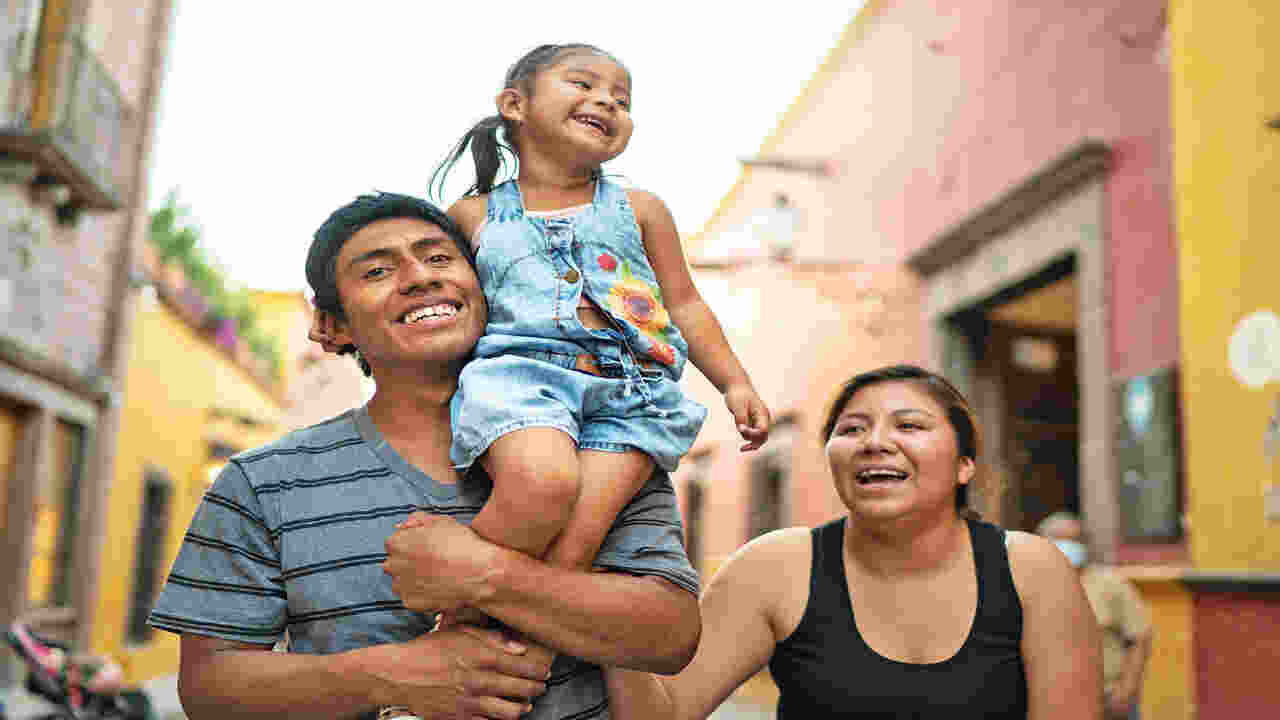

Family is an important part of Mexican culture and plays a vital role in society. Family provides stability and support to people in Mexican culture and plays a central role in their social and cultural life. Families are the center of Mexican society, and members expect to care for one another.
This family-oriented culture means unmarried women often take on a greater responsibility at home than men, sacrificing their career or professional goals to care for the family. As such, women in Mexican families often face gender-based discrimination and inequality.
However, families significantly reduce these inequalities by creating a sense of belonging and support within the family unit. This family-oriented culture also benefits children, who often grow up with extended family members such as grandparents or relatives. Family is an important part of Mexican culture that deserves appreciation and respect for its contributions to society.
The Traditional Gender Roles Of Men And Women In Mexican Culture

In Mexican culture, the roles of men and women are traditionally defined. Men provide financial support to the family, while women are typically responsible for caring for the home and children. While women in Mexican families often play a significant role in the community, it is rare to see a woman participate in high-level leadership roles.
The traditional adolescent gender roles of men and women in Mexican culture have remained largely unchanged for centuries. However, people are trying to shift these stereotypes and encourage more balanced roles between the sexes.
The Importance Of Extended Family In Mexican Culture
The importance of extended family in Mexican culture reflects the traditional role of the family. In Mexican society, families expect to care for one another and provide support during times of need. This is especially true for nuclear families, who rely on their extended families for social and economic support.
Family is a source of pride and responsibility for Mexicans, and members expect to contribute to the group’s well-being. As families play such an important role in Mexican origin culture, they play an important part in the socialization and development of children. Children learn about family values, gender roles, and other important topics through interactions with family members.
The Importance Of Religious Beliefs In Mexican Culture

The family is an important part of Mexican culture. It plays a central societal role and upholds traditional religious beliefs and practices. The family unit is responsible for supporting its members during times of need. In addition, the family is a source of strength and stability in Mexican culture.
Mexican culture considers religion an important part, and the family plays a significant role in supporting religious beliefs and practices in this regard. Families play a vital role in upholding religious diversity and ensuring that families can practice their faith openly and freely. Besides, families are responsible for supporting one another during times of need.
Mexican Women And Change
The role of the family in Mexican culture is changing. Women are leading successful lives both at home and in the workforce. Mexican women are breaking down traditional gender roles and expectations. They’re redefining what it means to be a strong, independent woman.
- Many young women pursue careers and education regardless of their family’s economic status.
- They’re also taking public stances on important issues such as reproductive rights and gender equality.
- In recent years, the Catholic Church has softened its stance on women’s roles in the church and society.
- As a result, more women enter leadership roles within the church hierarchy.
- Women have made significant gains in politics, business, and the arts.
- More women are providing leadership in science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM) than ever.
Education Shifts For Mexican Women
Mexican women have made significant progress in recent decades, but there is still a long way to go before women can achieve parity with men in every aspect of society. For example, education is a key factor that has helped Mexican women access employment and greater independence. However, women continue to face discrimination in education and employment, which limits their opportunities and reduces their chances for success.
Origins Of The Mexican Family

A married couple and their children compose the traditional Mexican family. The husband typically sweats the home, provides financial support for the family, and takes on most of the responsibilities associated with running the household. However, there has been a growing trend among Mexican families entering leadership roles within the church hierarchy in recent decades. This shift reflects women’s growing societal role and demand for greater equality within families and societies.
Indigenous Mexican Families
Indigenous Mexican families are the oldest type of family in Mexico. They descend from the ancient Aztec and Maya civilizations, which flourished over two thousand years ago. These families were among the first to migrate to Spanish colonies in the 16th century. Over time, indigenous Mexican families settled in different regions of Mexico, varying in size and structure.
Some remained in their traditional rural communities, while others moved to urban areas or other parts of the country. Through their long history as a nation, indigenous Mexican family culture families have retained their cultural identity and thrived as a vital part of society.
Catholic Influences On Mexican Family
The Mexican family reflects the Catholic Church’s influence on Mexican society. The family in Mexico City is traditionally patriarchal and nuclear, with the father as the head and the mother and children as subordinates. The family system is based on patrilineal descent, which means that the father is the head of the family.
This system reflects the Catholic Church’s teachings on family structure and social roles. The Mexican family is also popular for its high level of gender equality, with mothers and fathers sharing household chores and responsibilities equally.
The Traditional Mexican Family

The nuclear family unit characterizes the traditional Mexican family. The family comprises a father, a Mexican mother, and children. However, families include extended family members such as grandparents, aunts, uncles, and cousins. The family is patriarchal and patrilineal. Male members trace their lineage through the father’s side, making them the head of the family.
Marriage within the family is based on love and mutual respect. Families are very close-knit and support one another through thick and thin. Families come first in Mexican culture, especially among poorer families that rely on extended family members for financial support.
The family unit in Mexican culture emphasizes gender roles and responsibilities. Families rely on men to provide for their families, viewing them as breadwinners. Women are perceived as dutiful caretakers of the home and children. Thus, women cannot work outside their homes without their husbands’ consent. The traditional family structure helps families maintain their cultural core values of respecting gender roles and traditions of loving mothers and protective fathers.
Traditional Family Roles
In Mexican culture, the family is considered the foundation of society. The traditional family comprises a father, a mother, and their children. Roles within the family vary depending on the family’s socioeconomic status. Fathers are typically the head of the household and are responsible for financially supporting their families. Mothers are typically responsible for caring for the home and children, while fathers are often responsible for providing financial support and guidance to their children.
Men And Women
The traditional Mexican family is based on patria potestad or “father’s rule.” Under this system, fathers are the primary authority figures in the family and have the power to make decisions on behalf of their children. Mothers play an important role in the family, typically caring for the home and children, while fathers focus primarily on their careers.
In traditional families, men and women have equal societal roles and expect to contribute to their communities. As a result, families in Mexico strive to support one another and provide for their loved ones’ needs. The traditional Mexican family values mutual support, commitment, and respect despite its unique structure.
Multigenerational Households
In Mexican culture, the family is considered the foundation of society. Each family comprises a mother, a father, and their children. Multigenerational households are common in Mexican Latino culture, as families often choose to have multiple children to keep the lineage alive.
The traditional Mexican family is based on mutual respect and responsibility, with children expected to care for their parents and siblings. As a result, families tend to be close-knit and supportive of each other.
Children in Mexican families are encouraged to care for their parents and siblings, and elders are treated with respect and given opportunities to contribute to the community. Therefore, the traditional family structure offers its members many benefits and stabilizes society.
Large Extended Families
Traditional Mexican families are typically large and extended. Families can consist of between five and fifteen members, with parents being the head of the household. Mothers typically raise their children, and other female family members play a significant role in childbearing, child-rearing, and household management.
Fathers are traditionally away from home for work or to conduct family business, so mothers play an especially important role in the upbringing of their children. The traditional Mexican family is an integral part of Mexican culture, playing a vital role in social life. It is important to preserve the traditions and values of such families as we strive for cultural continuity.
Jefe De Familia
The jefe de familia is the head of the Mexican family. This position is inherited through the male line and typically corresponds to the father of the household. The jefe de familia is responsible for maintaining order within the family and ensuring that all members follow traditional values.
This important role involves managing family finances, overseeing important rituals and ceremonies, and ensuring family traditions follow. As a strong figure in Mexican culture, the jefe de familia is respected by all family members and plays an important role in their lives. In many families, he or she is a surrogate father and mother who provides guidance and support.
Intergenerational Transmission Of Values In Mexican Culture
The family is important in Mexican Latino culture, serving as the cornerstone of society. Within the family, individuals learn social and moral values, and traditions are passed down to future generations. Families provide vital support, offering love, stability, guidance, and security. They also shape individual character and instill strong moral values, promoting positive attitudes towards education and work.
Mexican families prioritize respecting elders and family members, teaching children to obey and care for them unconditionally. Family ties are deeply cherished beyond just the immediate unit encompassing society. This is evident through the intergenerational transmission of values and the active role of families in cultural production.
Conclusion
The family plays a central role in Mexican culture, serving as the foundation of society and providing support, love, and guidance to its members. From the extended family structure to the strong emphasis on respect for elders, Mexican families prioritize unity and connection. The importance of family is evident in various aspects of Mexican life, including celebrations, traditions, and values.
Understanding and appreciating the role of the family in Mexican culture can provide valuable insights into the rich tapestry of this vibrant society. So next time you celebrate with loved ones or partake in a cultural tradition, remember the significance of family and cherish those special moments together.
Frequently Asked Questions

I’m a writer and blogger who loves to talk about entertainment, culture, and relationships. I love to share my thoughts and insights on these topics, and I’m always looking for new ways to engage with my readers. I’m also a big fan of learning new things, so I’m always exploring new areas of interest.
