The Celts and Vikings are two ancient civilizations that have captured the imagination and fascination of people for centuries. These two groups, with their unique cultures and beliefs, have left a lasting impact on the history and development of Europe.
From their fierce warriors to their rich mythology, the Celts and Vikings continue to intrigue and inspire people worldwide. Despite their similarities in some aspects, the Celts and Vikings were distinct groups with distinct traditions, beliefs, and ways of life.
Here, we will explore the similarities and differences between the Celts and Vikings, exploring their origins, cultures, and legacies. So, let us journey through time to explore the fascinating world of the Celts and Vikings and unravel the mysteries and complexities of their existence.

Who Were Celts?
The Celts were a group of ancient peoples who inhabited much of Europe during the Iron Age. They were popular for their distinct culture, which included a unique language, art, and religious practices. The Celts, skilled warriors, often engaged in warfare with neighbouring tribes and even the Roman Empire.
They also had a strong connection to nature and believed in the existence of spirits and gods. Despite being conquered by various empires throughout history, Celtic culture and traditions have continued to influence modern-day societies in regions such as Ireland, Scotland, Wales, and Brittany.
Historical Background Of The Celts And Vikings
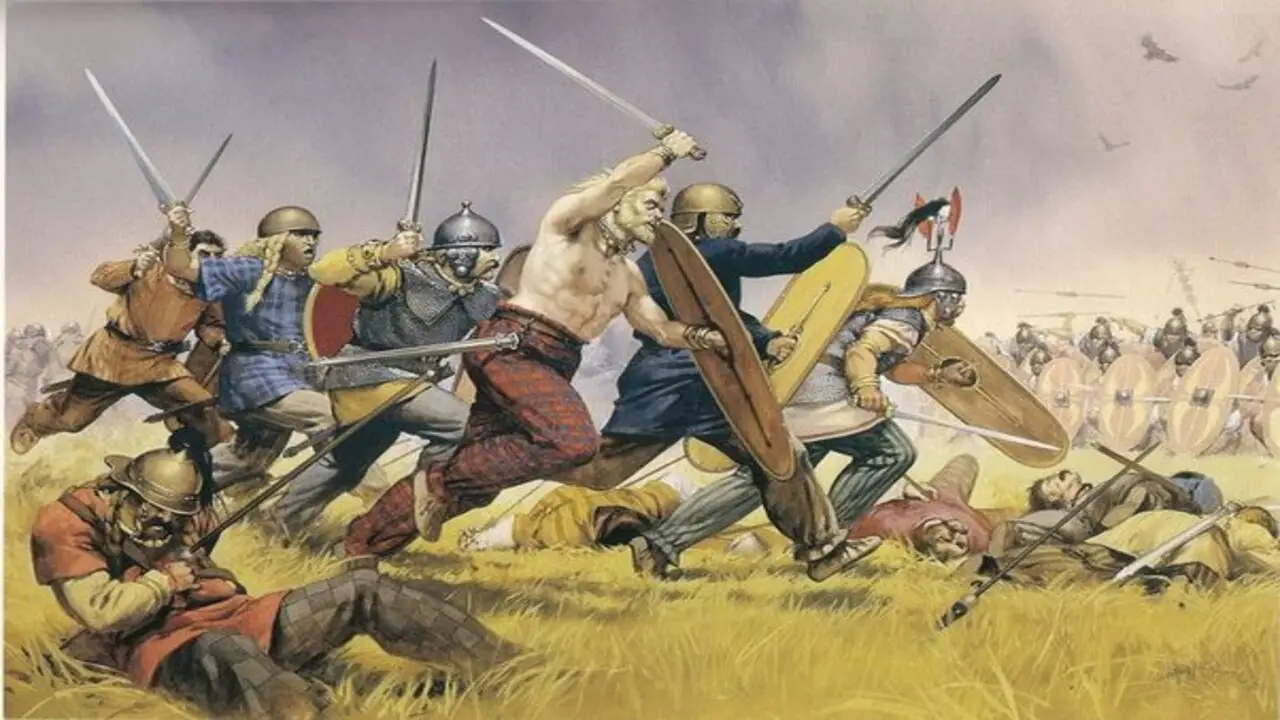

The Celts and Vikings were two distinct groups with different historical backgrounds. The Celts, who inhabited parts of Europe during the Iron Age, were popular for their advanced metalworking skills and artistic culture. They organized their society into tribes and had a complex social structure.
On the other hand, the Vikings were seafaring warriors from Scandinavia who emerged during the Viking Age. They were proficient navigators and traders but also notorious raiders. Known for their longships and fearsome reputation in battle, they significantly impacted European history by exploring and colonizing new lands. While the Celts and Vikings left a mark on history, their cultures, traditions, and influences were distinct.
Celts Vs Vikings – The Similarities & Differences
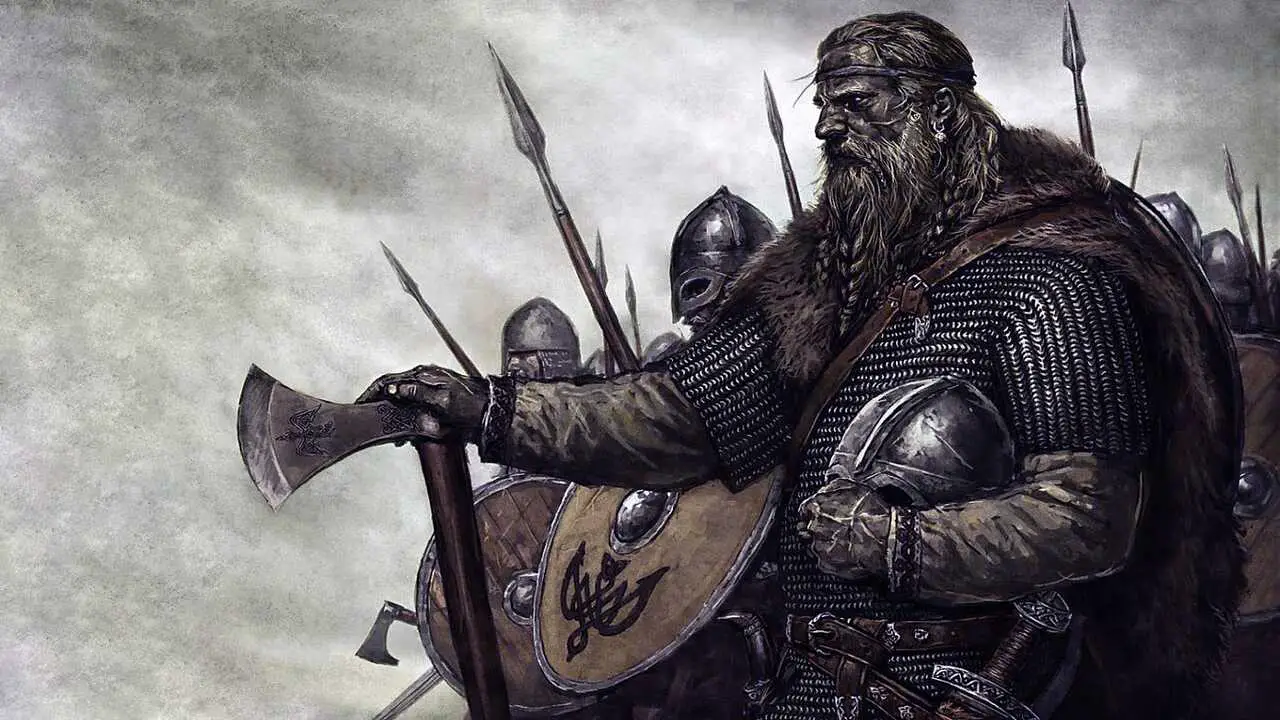

When examining the Celts and Vikings, it becomes clear that while there are some similarities between these two ancient civilizations, significant differences set them apart. The Celts and Vikings were famous for their warrior culture, but their approaches to warfare differed greatly.
The Celts were popular for their fierce and organized tribes, with a complex social structure and a strong emphasis on honour and bravery in battle. On the other hand, the Vikings were highly proficient seafarers and raiders with a more individualistic approach to combat.
1.Warfare And Battle Strategies Of The Celts And Vikings
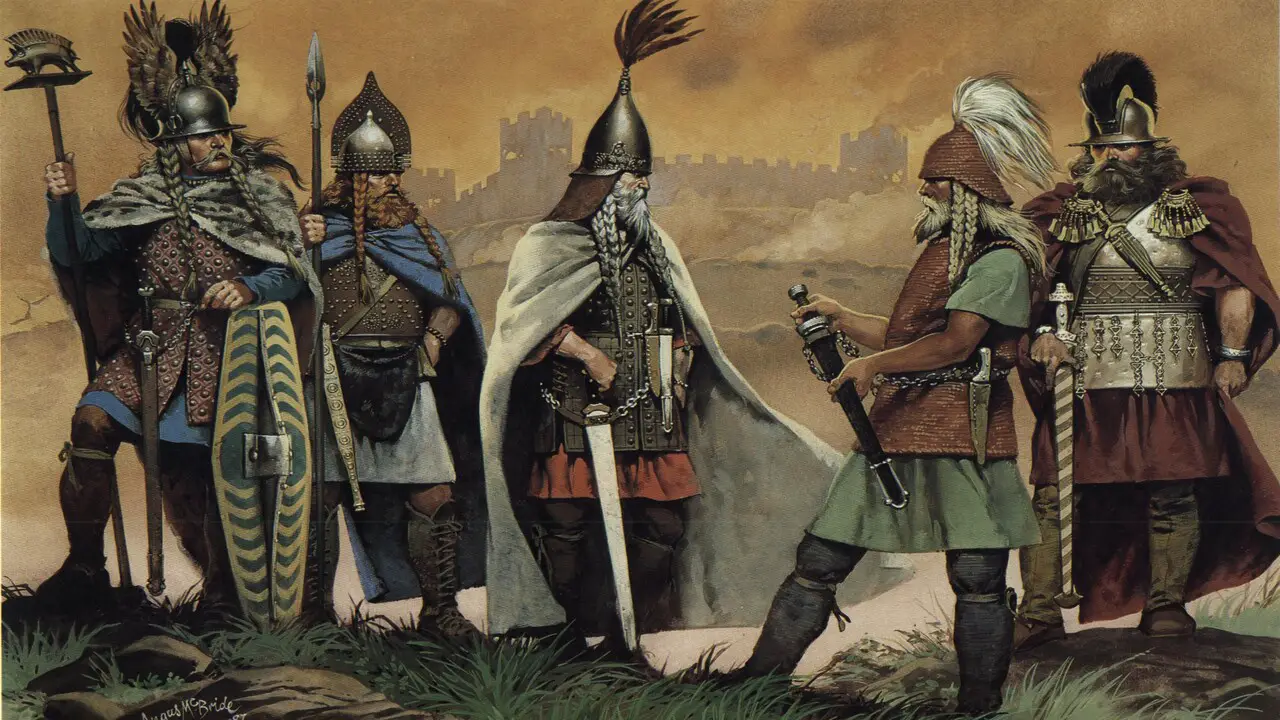

The Celts and Vikings had distinct warfare and battle strategies that reflected their respective cultures and societies. The Celts, known for their bravery and ferocity in battle, often relied on hit-and-run tactics and guerrilla warfare. They favoured ambushes, skirmishes, and surprise attacks to disrupt enemy forces.
On the other hand, the Vikings were highly proficient seafarers and raiders who utilized their longships to launch swift and devastating attacks along coastal areas. They were popular for using superior naval tactics, such as boarding enemy ships or beaching their boats quickly for land-based assaults. While both civilizations had unique approaches to warfare, they shared a common emphasis on courage and martial prowess, making them formidable opponents in the ancient world.
2.Weapons And Armor Used By The Celts And Vikings
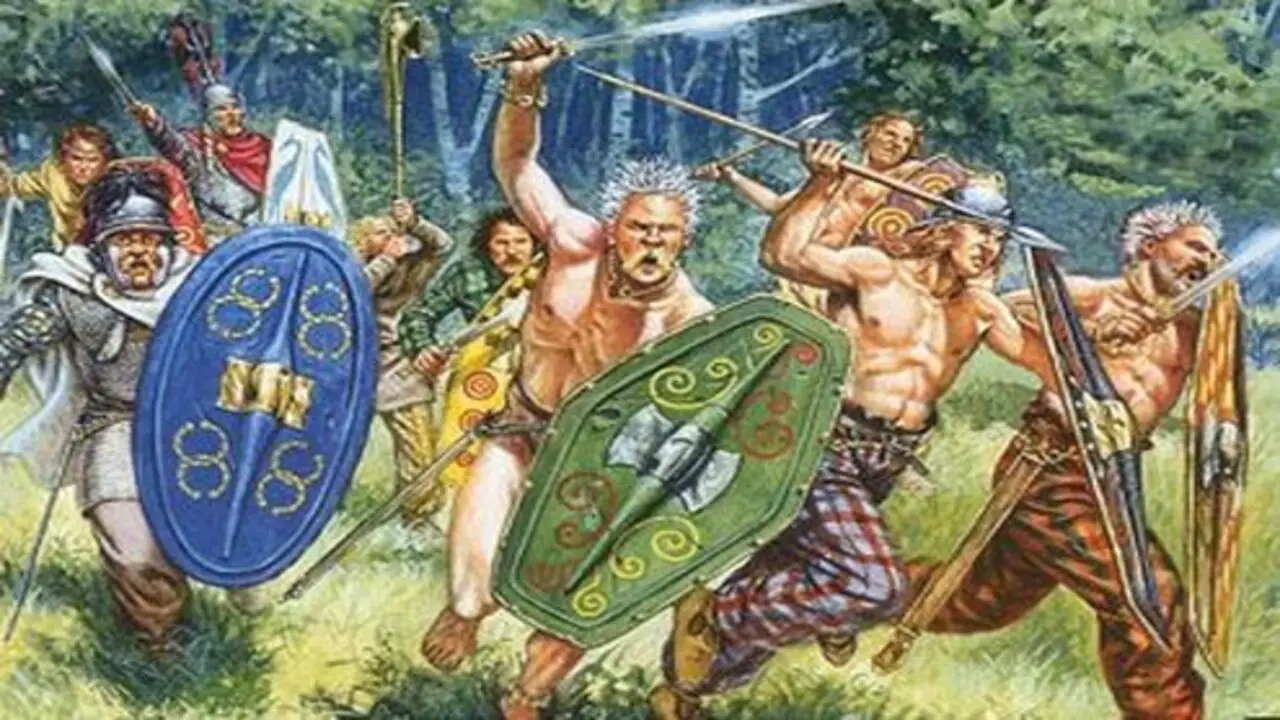

The Celts and Vikings utilized various weapons and armor in battle, showcasing their skills as skilled warriors. The Celts were popular for using long swords, spears, and shields. They also wore chainmail armour and helmets for protection. In contrast, the Vikings favoured using axes, swords, and round shields.
They were also popular for their iconic Viking longships, which enabled them to conduct raids and travel long distances. Regarding armour, the Vikings typically wore chainmail shirts or leather armour, along with helmets adorned with intricate designs. While the two groups had similarities in weaponry and armour, each had its unique style and battle techniques.
3.Impact Of The Celts And Vikings On European History
The Celts and Vikings played significant roles in European history, although they were distinct cultures with unique characteristics. The Celts were an ancient group of people who inhabited much of Europe during the Iron Age. They were popular for their skilled craftsmanship, intricate artwork, and spiritual beliefs.
On the other hand, the Vikings were seafaring warriors from Scandinavia who raided and settled in various parts of Europe during the Viking Age. They were famous for their shipbuilding skills, exploration, and military prowess.
Both civilizations profoundly impacted European history through cultural influence, trade networks, and interactions with other societies. While they share some similarities in terms of their warrior traditions and storytelling traditions, the Celts and Vikings also have distinct differences in their art styles, social structures, and geographic origins.
4.Trade And Interactions Between The Celts And Vikings
The Celts and Vikings both played significant roles in shaping European history. The Celts, who inhabited areas of Europe from around 1200 BC to 400 AD, were popular for their advanced metalworking techniques and distinctive art styles. They had a complex social structure and were proficient warriors.
On the other hand, the Vikings emerged around the late 8th century and were famous for their seafaring abilities and raids on coastal communities. They established settlements across Europe, including in Ireland, Scotland, England, and France. Both groups profoundly impacted the regions they inhabited, influencing language, culture, and even political structures. While there are similarities between the Celts and Vikings regarding their warrior cultures and influence on European history, they also have distinct differences in their origins and societal structures.
5.Mythology And Religious Beliefs Of The Celts And Vikings
The mythology and religious beliefs of the Celts and Vikings share some similarities but also have distinct differences. Both cultures had a pantheon of gods and goddesses, with each deity representing different aspects of nature and human life.
However, the Celts placed a strong emphasis on the spiritual world and believed in the existence of supernatural beings such as fairies and spirits. On the other hand, the Vikings focused more on warrior gods and their exploits in battle. Additionally, while both cultures practised ritual sacrifices, the Celts often sacrificed animals, while the Vikings primarily sacrificed humans. These differences in mythology and religious practices highlight the unique cultural identities of both the Celts and Vikings.
6.Famous Leaders And Figures From Both Cultures
The Celts and Vikings were famous for their strong leaders and influential figures. In Celtic culture, leaders were often chosen based on bravery, strength, and wisdom. One famous Celtic leader was Boudicca, who led a rebellion against the Roman Empire in ancient Britain. She for her fierce determination and refusal to back down.
On the Viking side, legendary figures like Ragnar Lothbrok and Erik the Red are well-known for their explorations and conquests. These leaders played significant roles in shaping the Viking Age and leaving a lasting impact on history. While both cultures had distinct leaders, they shared a common thread of valuing strength, courage, and strategic thinking.
7.Legacy Of The Celts And Vikings In Modern Times
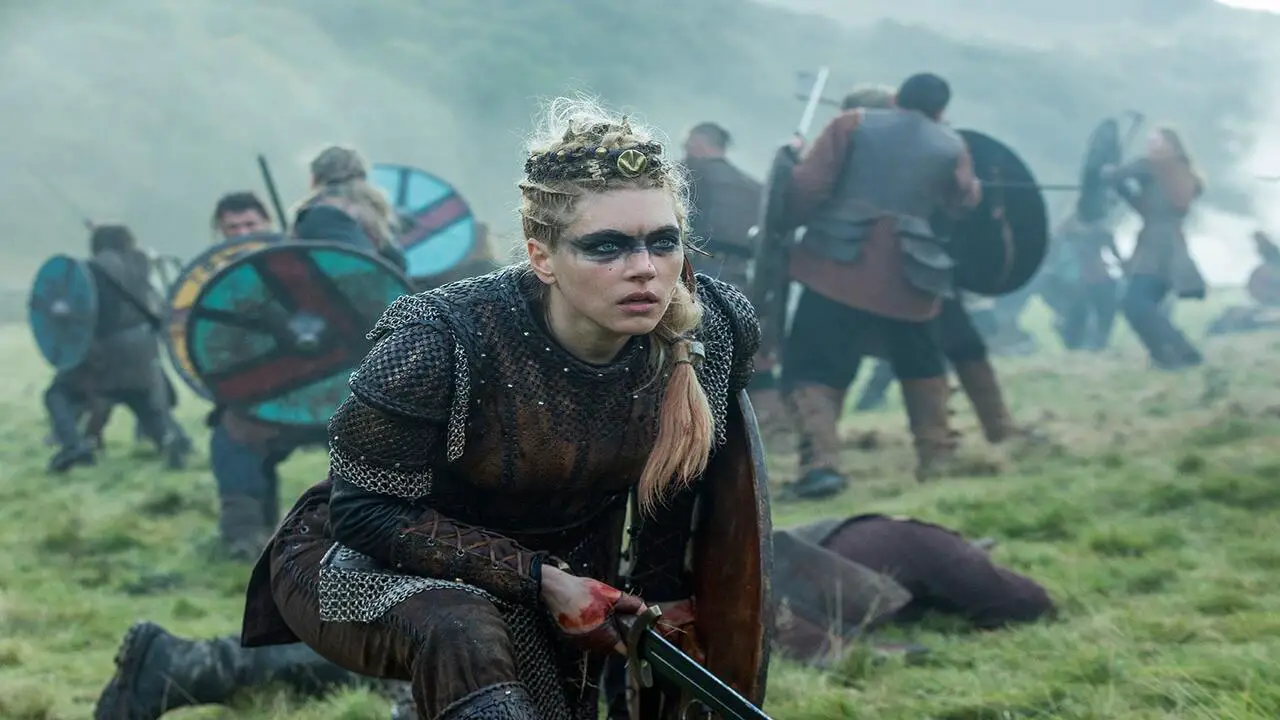

The legacy of the Celts and Vikings can still be seen in modern times, although they existed centuries ago. Both cultures have significantly impacted language, art, and folklore. The Celts, known for their intricate knotwork designs and mythical stories, have influenced modern Celtic art and music.
On the other hand, the Vikings are popular for their seafaring skills and exploration. Their influence can be seen in the names of cities and towns along the coastlines they once raided and settled. Additionally, both cultures have left a lasting impact on the languages spoken in their respective regions. Irish and Scottish Gaelic have roots in Celtic languages, while Old Norse has influenced modern Scandinavian languages.
Why Did The Terrible Viking Warriors Move Away From Scotland?
The Viking warriors, known for their fearsome reputation, eventually moved away from Scotland for various reasons. One significant factor was the decline in their regional influence and power. As the Scottish kings consolidated their control, the Vikings faced increasing resistance and could no longer maintain their strongholds.
Additionally, changes in trade routes and the rise of other Viking settlements further south provided new opportunities for expansion and plunder. The Vikings may have also faced internal conflicts or pressures from neighbouring groups. Ultimately, these factors likely contributed to their decision to move away from Scotland and seek new territories to conquer.
Appearing In The Timeline Of The Medieval History
The timeline of medieval history is a complex tapestry of events and developments that shaped the course of Europe and beyond. From the 5th to the 15th century, this period witnessed the rise and fall of great empires, the spread of Christianity, the emergence of feudalism, and the flourishing of art, literature, and science.
One significant event in the timeline is the fall of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th century, marking the end of classical antiquity and the beginning of the Middle Ages. This led to a power vacuum, allowing new kingdoms to rise and establish feudalism. Another pivotal moment is the Crusades in the 11th to 13th centuries. These religious wars were initiated by European Christians to reclaim the Holy Land from Muslim control, resulting in trade expansion and cultural exchange in Europe.
The Way Of Life
The Celts and Vikings had distinct ways of life that were shaped by their respective cultures and environments. For the Celts, life revolved around tribal communities and agriculture. They were proficient farmers, growing barley, oats, and wheat crops and raising livestock like cattle, sheep, and pigs.
They lived in small settlements known as ringforts or hillforts, often surrounded by defensive walls. Celtic society was organized into clans or tribes, with a chieftain as the leader. They had a strong warrior culture and engaged in warfare for defence and raiding.
On the other hand, the Vikings were seafaring people who relied heavily on trade and exploration. They were proficient shipbuilders and navigators, allowing them to venture far from their homelands and establish settlements in new lands. They were popular for their raiding and pillaging, targeting monasteries, villages, and coastal towns.
‘More Civilized’
When comparing the Celts and Vikings, it is important to note that the concept of being “more civilized” is subjective and can be influenced by cultural biases. However, certain aspects of both cultures can be seen as more advanced or sophisticated.
The Celts had a well-developed society with complex social structures and intricate artwork. They had a hierarchical system with chieftains leading their tribes and skilled craftsmen creating beautiful metalwork, jewellery, and intricate designs on their weapons and clothing. They also had a rich mythology and oral tradition, with bards and druids playing important societal roles.
On the other hand, the Vikings were popular for their advanced shipbuilding techniques, which allowed them to navigate the treacherous seas and explore new lands. They also had a sophisticated legal system known as the Thing, a governing body for their settlements. Additionally, they strongly believed in personal honour and reputation, with warriors striving to achieve fame and glory through bravery in battle.
Art And Influences
Both the Celts and Vikings had unique artistic traditions that left a lasting impact on their respective cultures and beyond.Celtic art is characterized by intricate designs and patterns, often featuring interwoven knots, spirals, and zoomorphic motifs. These designs were commonly found in metalwork, such as jewellery, weaponry, and religious objects. The craftsmanship of Celtic artists was highly regarded, and their art significantly influenced later medieval art styles.
On the other hand, Viking art was popular for its bold and dynamic designs. They often incorporated animal motifs, including dragons, serpents, and geometric patterns. Viking artists excelled in metalwork, creating intricate jewellery, weapons, and everyday objects.
Disappearance
The Celts and Vikings experienced a decline and eventual disappearance from the historical stage. For the Celts, their power and influence began to wane with the Roman conquest of Gaul in the 1st century BCE. As the Roman Empire expanded, Celtic territories were gradually assimilated into Roman culture and society.
The process of Romanization led to the adoption of the Latin language, Roman law and customs, and the decline of Celtic languages and traditions. Additionally, the arrival of Germanic tribes such as the Angles, Saxons, and Jutes in Britain further marginalized Celtic influence.
As for the Vikings, their era of exploration and raiding began to decline with increased resistance from local populations and the establishment of more centralized kingdoms in Europe. The conversion of many Vikings to Christianity also played a role in their cultural assimilation and the decline of their Norse traditions. The Viking Age ended with the Norman Conquest of England in 1066. Which marked the beginning of a new era in European history.
British Or Irish Reached Remote Islands Before Vikings
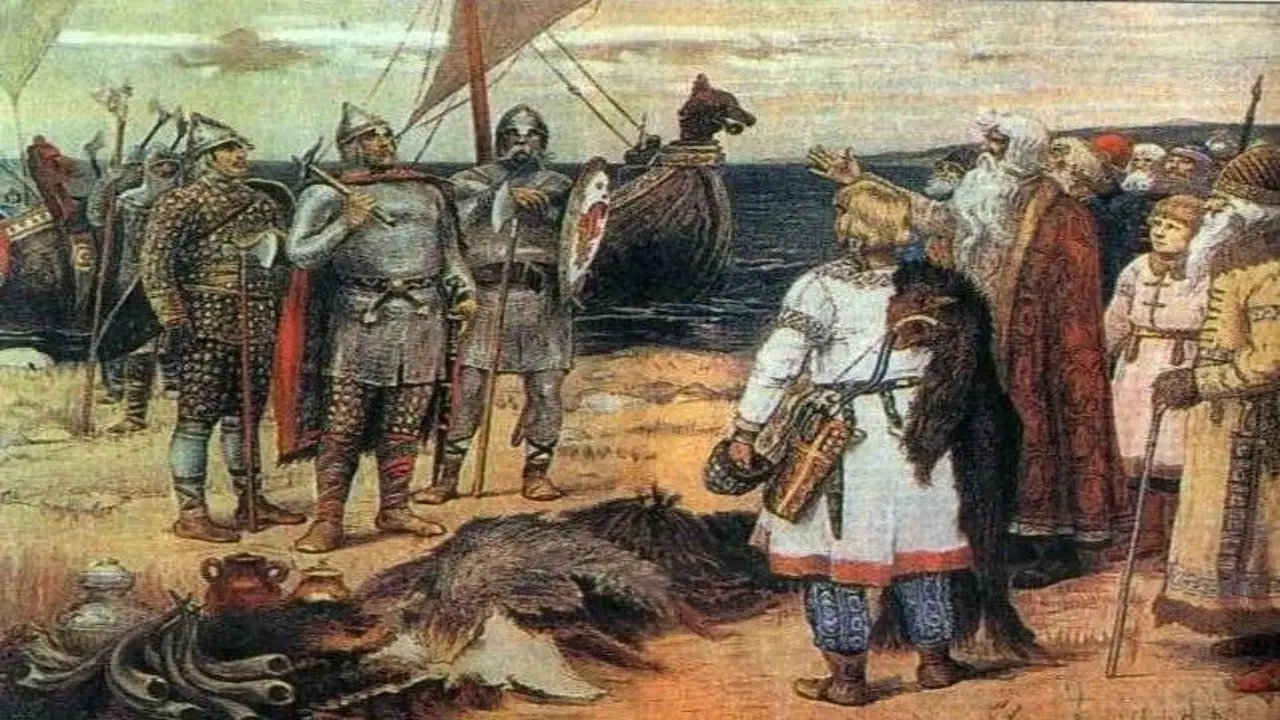

Evidence suggests that British or Irish people may have reached remote islands before the Vikings. Archaeological discoveries on islands such as St. Kilda, the Outer Hebrides, and the Faroe Islands have revealed early settlements dating back to the 6th and 7th centuries.
These settlements contain artefacts and structures that indicate a connection to British or Irish cultures. While it is still a topic of debate among historians and archaeologists, these findings challenge the traditional narrative of Viking exploration and settlement in these areas. Further research and excavation are needed to fully understand the extent of early British and Irish presence on these remote islands.
Conclusion
The Celts and Vikings may have lived in different periods, but shared some fascinating similarities and differences. Both civilizations were famous for their fierce warriors and distinctive cultures. While the Celts had a complex society with powerful druids and a rich mythology.
The Vikings were renowned for their seafaring skills and daring raids. Despite these differences, both groups valued honour, bravery, and loyalty. By exploring their histories, we can gain a deeper understanding of the diverse tapestry of human civilization. Whether you’re drawn to the mysticism of the Celts or the adventurous spirit of the Vikings, their legacies continue to captivate us today.
FAQs
Is it True That Vikings Raided the Celts?
The reality is that raids occurred in both directions, and the Norse had every cause to fear their Celtic neighbors. There were Viking attacks reported in Wales, as well as traces of minor colonies.
The Norse were finally driven out of Scotland. But ultimately, Celts and the Vikings had to get along.
Are The Celts considered Vikings?
Celts were not generally Vikings, but Norse Gaels were created by inter-marital interaction and cultural interaction between the Celtic and the Norse Vikings. Most Icelanders and Faroes are North Viking ancestors and Celtic slave women kidnapped from England and Germany.
What Is The Relationship Between Vikings And Celts?
There is no clear answer to this question, as the relationship between Vikings and Celts is a subject of debate. Some sources claim that the two groups were enemies, while others claim that they had a more complex relationship. What is generally agreed upon, however, is that the Viking raids on the Celtic settlements were frequently destructive and led to a great deal of bloodshed.
There is no one-size-fits-all answer to this question, as the relationship between Vikings and Celts varied depending on the time and place. Generally speaking, though, the two groups fought each other sporadically throughout the course of their history.
There are a few instances where Vikings and Celts cooperated against other groups, but these were rare exceptions. In general, their interactions were often negative and destructive.
How Would You Rate Your Experience Shopping For Books On Amazon Today?
Amazon is one of the most popular online shopping destinations in the world, and for good reason. They offer an incredible selection of books that is sure to meet your needs and more. Here are some my tips for how to shop for books on Amazon:
Read the reviews – It’s important to read the reviews before you buy a book, especially if you’re not familiar with the author or the genre. This will help you get a better idea of what to expect and whether or not the book is worth your purchase.
Compare prices – It’s always a good idea to compare prices before making a purchase. Not only will this help you save money, but it will also give you an idea of what type of book (fiction or non-fiction) is selling well and what might be a better value for your money.
Check out Kindle Unlimited – Kindle Unlimited is an Amazon exclusive service that allows customers to read unlimited amounts of books for free. This can be a great way to sample new books before making a purchase.
Try Audible – Audible is another great option for audio books. With this service, you can listen to books on your computer, phone, or tablet. This can be great for commuters who want to listen to a book while they’re on their way home from work.
With these tips in mind, shopping for books on Amazon should be easy peasy! Thanks for asking!
Norse Vs Celtic Paganism || Which Pagan Path Is Best For You?
There are many different Pagan paths out there, and which one is right for you depends on a lot of factors, including your personal beliefs and preferences. That being said, here are two popular Pagan paths that might be of interest to you:
Norse Paganism – This path is based on the beliefs of the Norse gods and goddesses, who are often seen as the ancestors of modern-day paganism. The path emphasizes nature worship, Dark Moons spiritual work, and rune casting.
Celtic Paganism – This path focuses on the Celtic pantheon of gods and goddesses, who are believed to have influenced modern paganism in some way or another. The path emphasizes nature worship, solar magic, and divination.

I’m a writer and blogger who loves to talk about entertainment, culture, and relationships. I love to share my thoughts and insights on these topics, and I’m always looking for new ways to engage with my readers. I’m also a big fan of learning new things, so I’m always exploring new areas of interest.
