Prussia, a historical region in northeastern Europe, has a vibrant culture that has influenced the development of the modern world. We will delve into the unique facets of Prussian culture, exploring its history, traditions, and customs.
Prussia was first established as a German territory in the 12th century. Over the years, it grew to encompass a vast area, including the regions of Brandenburg, Pomerania, and Royal Prussia.
Under the rule of prominent leaders such as Frederick William and Albert Frederick, Prussia became a dominant power in Europe, leaving a lasting legacy that can still be seen in modern-day Germany.
By examining the key elements of Prussian culture, we can better understand the people who inhabited this territory and their impact on the world. So, let us embark on a journey to discover the rich and diverse world of Prussian culture and its lasting influence on the global stage.

Historical Background And Origins Of Prussian Culture
Prussian culture has its roots in the historical region of Prussia, which was located in modern-day Germany and Poland. Various tribes and ethnic groups inhabited the area during the early medieval period, tracing the origins of Prussian culture back to that time. Over time, the region came under the rule of the Teutonic Knights, who significantly shaped Prussian culture through their influence on architecture, religion, and governance.
In the 18th and 19th centuries, Prussia emerged as a powerful kingdom under the leadership of Frederick the Great, further contributing to the development of Prussian culture. Today, German and Polish society still show elements of Prussian culture in various aspects, including traditions, art, and architecture.
Key Characteristics And Values Of Prussian Culture
Prussian culture, known for its distinct and influential characteristics, holds a rich tapestry of values that have shaped its society and legacy. One of the key characteristics of Prussian culture is its emphasis on discipline and order.
Embedded in the Prussian ethos is a deep-rooted belief in the importance of structure and hierarchy, which has guided their approach to governance, education, and military strategy. This commitment to discipline has allowed Prussia to thrive and become a formidable force in European history.
Traditional Customs And Rituals In Prussian Culture
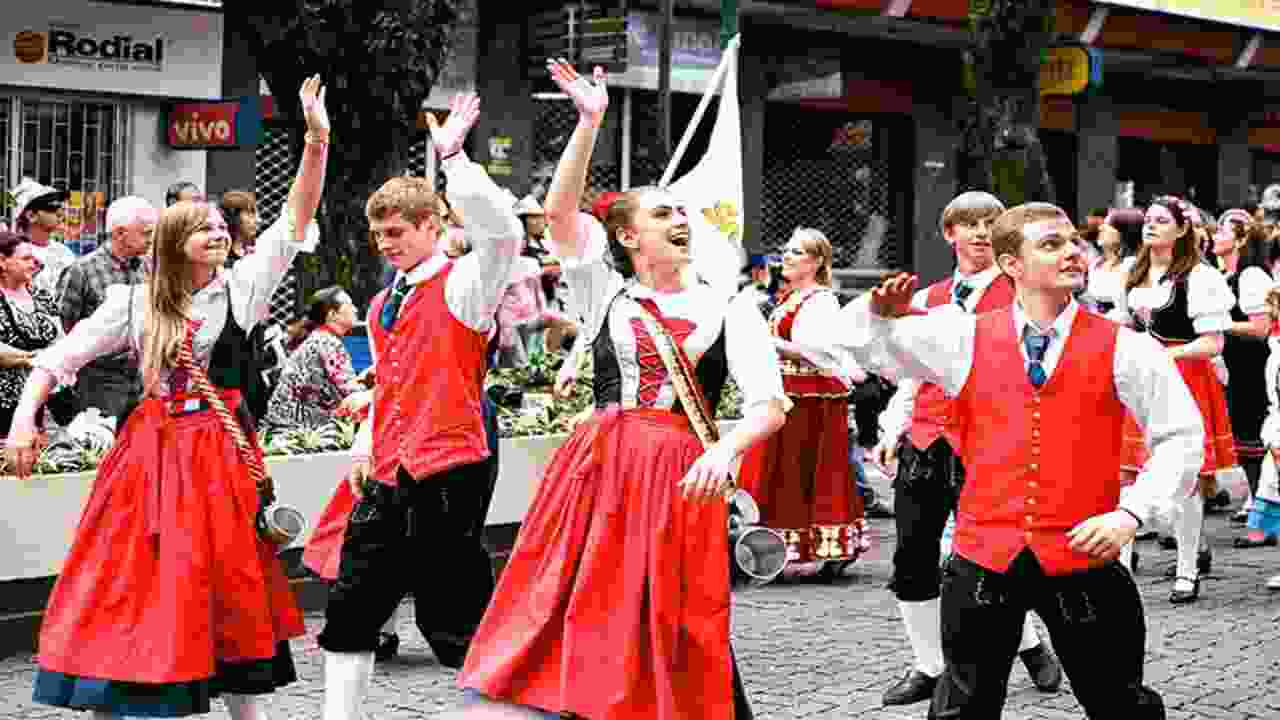

Traditional customs and rituals played a significant role in Prussian culture, particularly during the reign of Frederick William, who ruled over the German territory. One notable aspect of Prussian culture was the strong emphasis on discipline and order. The authorities instilled values of punctuality, obedience, and respect for authority in the Prussians from a young age.
The state placed significance on military service and loyalty. People highly regarded the Prussian army and saw it as a symbol of national pride. Additionally, Royal Prussia, which encompassed parts of modern-day Poland and Russia, had distinct customs and traditions influenced by Polish and German cultures. These traditional customs and rituals were crucial in shaping Prussian culture and identity.
Art, Literature, And Music In Prussian Culture
Art, literature, and music played a significant role in Prussian culture. During the reign of Albert Frederick, the arts flourished in Prussian territories. The Prussian court became a hub for talented artists, writers, and musicians, attracting talent from all over Europe. Artists like Hans Holbein the Younger and Albrecht Durer produced notable works during this time, while poets like Johann Wolfgang von Goethe and Friedrich Schiller emerged as prominent figures in German literature.
Composers such as Ludwig van Beethoven and Carl Maria von Weber were influenced by Prussian culture in music and made important contributions to the classical music scene. Modern-day Germany celebrates the legacy of Prussian art, literature, and music.
Prussian Cuisine And Traditional Food
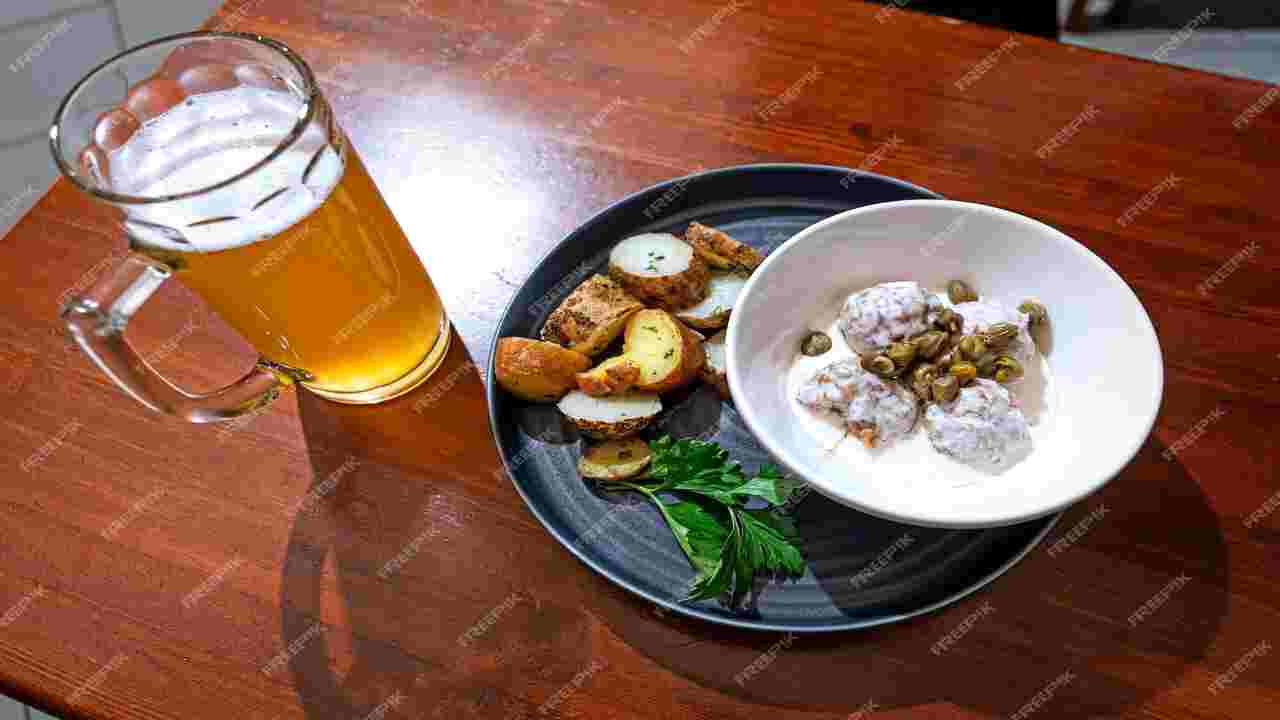

Prussian cuisine and traditional food are deeply rooted in the culture and history of Prussia, reflecting the values and traditions of the North German region. The cuisine is popular for its hearty and wholesome dishes, often featuring potatoes, cabbage, pork, and fish. Popular dishes include sauerkraut, kohlwurst (cabbage sausage), and Königsberger Klopse (meatballs in a white sauce).
Leaders such as Frederick the Great upheld the Prussian virtues, also reflected in Prussian cuisine. Prussian cooking reflects these virtues, including discipline, loyalty, frugality, and diligence, in its simplicity and practicality. Overall, Prussian cuisine offers a taste of history and tradition, providing insight into the cultural heritage of this influential region.
Educational System
The educational system in Prussia was known for its emphasis on discipline, order, and academic rigor. Education was seen as a means to instill values of loyalty, obedience, and duty in the younger generations. The Prussian education system played a significant role in shaping the country’s society and producing skilled workers, administrators, and military personnel.
One of the key features of the Prussian educational system was its centralized and standardized approach. The state had control over the curriculum, ensuring that students received a uniform education regardless of their social background or location. This system aimed to create a cohesive society with shared values and principles.
Festivals And Celebrations In Prussian Culture
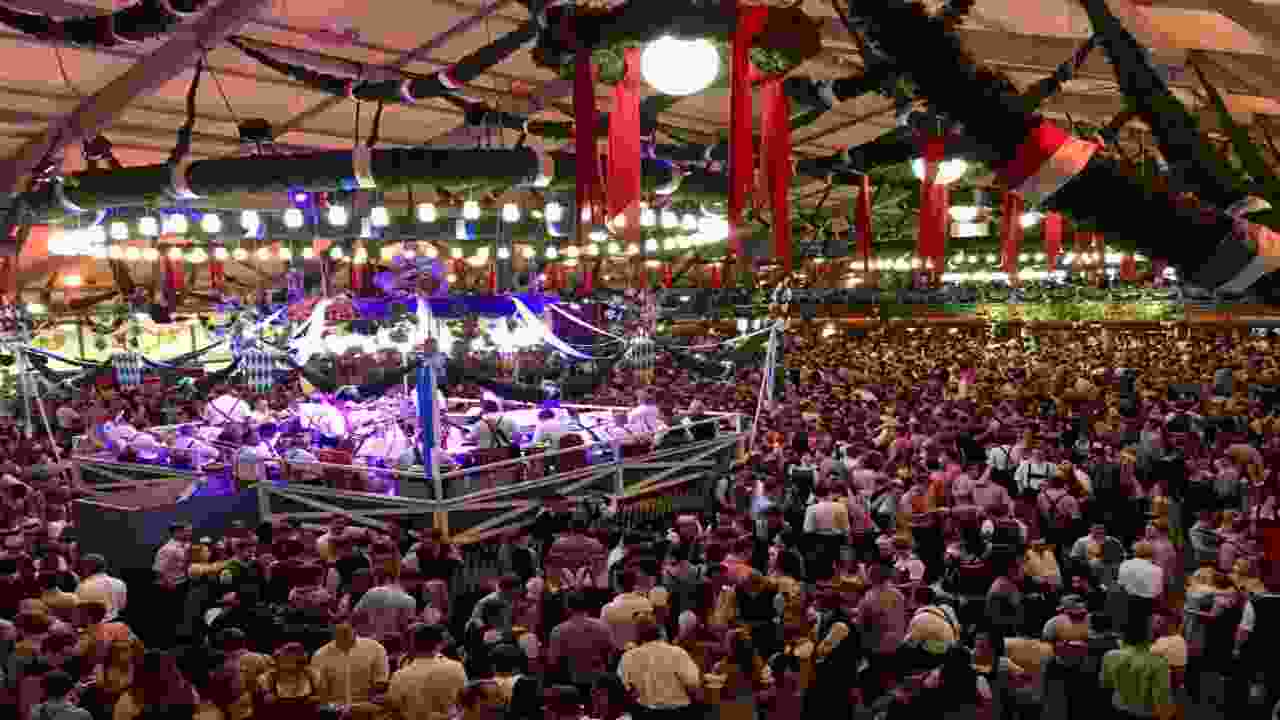

In Ducal Prussia, festivals and celebrations were important to Prussian culture. These events allowed the community to unite and celebrate their shared traditions and values. Festivals such as Harvest Festival and Christmas were particularly significant. They marked important milestones in the agricultural and religious calendars, respectively. Additionally, under federal and later Imperial control, these festivals took on a more unified and standardized format.
The government played a larger role in organizing and overseeing them. This helped to create a sense of unity and cohesion within Prussian society. Overall, festivals and celebrations played a crucial role in preserving and promoting Prussian culture while fostering community and identity among its people.
Influences On Contemporary German Culture
Prussian culture has had a significant influence on contemporary German culture. Some key characteristics and values of Prussian culture include discipline, orderliness, and a strong emphasis on education and intellectual pursuits. These values have become ingrained in German society, shaping how people approach work, education, and interpersonal relationships.
Additionally, Prussian militarism and the concept of duty left a lasting impact on German society, emphasizing loyalty and honour. And a sense of responsibility towards the greater good. People can still see these cultural influences today in various aspects of German life, from the efficient bureaucracy to the high value placed on punctuality and reliability.
Preserving And Promoting Prussian Cultural Heritage
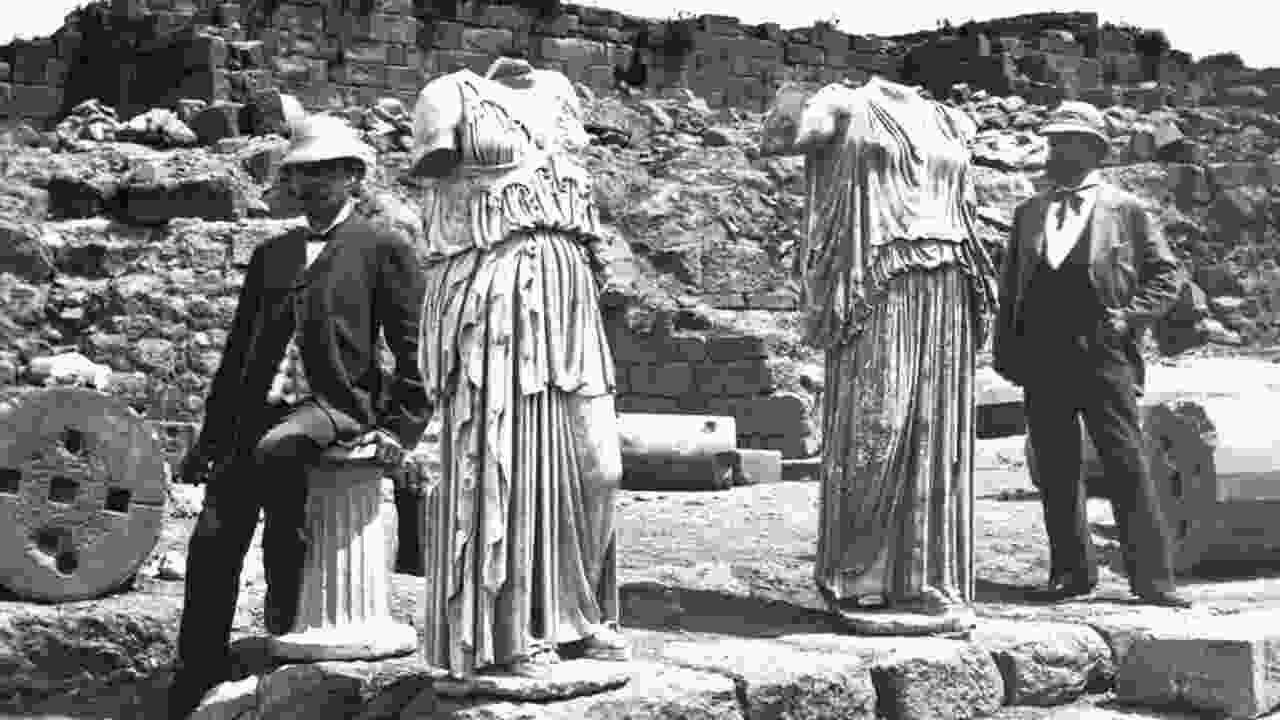

Preserving and promoting Prussian cultural heritage is important to keep the traditions and values of Prussian culture alive. Prussian culture’s key characteristics and values include discipline, efficiency, and a strong sense of duty. Prussians value hard work, education, and orderliness.
They deeply respect authority and place high importance on loyalty and honour. By preserving and promoting Prussian cultural heritage, we can ensure that these important characteristics and values continue to be passed down through generations, contributing to the rich tapestry of human history.
Belief
Religion played an important role in Prussian culture, with Christianity, particularly Protestantism, being the dominant faith. The Prussian Union was established in 1817, which merged the Lutheran and Reformed churches in Prussia. This union aimed to create a more unified religious identity and promote cooperation among different Christian denominations.
Prussians placed a strong emphasis on moral values and ethics, influenced by their Christian beliefs. They believed in living a virtuous and upright life, guided by principles of honesty, integrity, and compassion. These values were instilled in the education system and were seen as essential for maintaining a harmonious and orderly society.
The Prussian belief in duty and loyalty extended beyond religious aspects. It was ingrained in their social, political, and military structures as well. Pruss ians saw it as their duty to serve the state and fulfill their responsibilities towards their community and nation. Loyalty to the king or emperor was highly valued, and individuals were expected to prioritize the needs of the state over their personal desires.
Conclusion
Prussian culture is rich in history and values that have shaped the region’s identity. From its emphasis on discipline and order to its appreciation for education and intellectual pursuits, Prussian culture is known for its strong work ethic and commitment to excellence. The values of loyalty, honour, and respect are deeply ingrained in Prussian society, creating a sense of unity and pride among its people.
Whether it’s the renowned Prussian military tradition or the cultural contributions in art, music, and literature, Prussian culture continues to influence and inspire. Exploring the key characteristics and values of Prussian culture provides valuable insights into the unique heritage of this fascinating region.
FAQ
What Culture Were The Prussians?
The Prussians were an ancient Baltic tribe living in what is now modern-day Poland and Lithuania. They had their distinct language and culture. But they were eventually assimilated into the Germanic culture after the Teutonic Knights conquered their territories in the 13th century.
What Is Prussia Most Known For?
Prussia is most known for being a prominent European power during the 18th and 19th centuries. It played a major role in the unification of Germany under Otto von Bismarck. It was popular for its disciplined and efficient military and philosophy, art, and education contributions.
What Is The Main Religion In Prussia?
The main religion in Prussia was Protestantism, particularly the Lutheran denomination. However, there were also significant populations of Catholics and other religious minorities in different regions of Prussia.
Which Country Is Prussia Now?
Prussia no longer exists as a country. After World War II, the territory of Prussia was divided among several countries, including Germany, Poland, Russia, and Lithuania.
Why Was Prussia So Powerful?
Prussia was powerful because it had a strong military, effective bureaucracy, and a centralized government. It also benefited from significant territorial acquisitions, skilled leadership, and a focus on modernization and industrialization.

I’m a writer and blogger who loves to talk about entertainment, culture, and relationships. I love to share my thoughts and insights on these topics, and I’m always looking for new ways to engage with my readers. I’m also a big fan of learning new things, so I’m always exploring new areas of interest.
